Tesla is currently the 11th largest company in the world, with annual revenue of 100 billion dollars. In less than two decades, it has surpassed industry giants, created a market that didn’t exist before – transportation powered by solar energy batteries – and now produces 1.8 million cars per year, aiming to reach 10 million in the near sustainable future.

The Arrival of Musk
Tesla Motors was founded in California in 2003 by two Silicon Valley engineers to produce electric sports cars. At that time, there was already concern about fossil fuels, but the idea of an electric car seemed unfeasible.
The following year, in 2004, Elon Musk invested $6.5 million in the company, and he would invest ten times that amount in the following years, becoming the largest shareholder with 20% of the shares. In the first five years, the company focused on securing private investors to finance research and development, facing various technical and financial challenges.
In 2008, the original partners left the management, and Elon Musk became CEO, taking drastic measures to prevent Tesla from going bankrupt, such as cutting 1/4 of the workforce and securing half a billion dollars in loans. In the same year, Tesla launched its first model, the Roadster, which proved the viability of an electric sports car, with a range of almost 400 km per charge.

IPO and the First Models
2,500 units of the Roadster were produced during the 4 years it was in production, and it is now a collector’s item: a used one is sold for 2.5 times the original price of $100,000. Today, Tesla sells 700 times more cars than that, but the Roadster was a game-changer, kicking down the door of the industry and making Tesla the first car manufacturer to go public on the American stock exchange since Ford’s IPO in 1956.
In Tesla’s IPO in 2010, ticker TSLA, 13.3 million shares were issued at $17 each, and by the end of the day, they had already risen by 40%. Thus, they raised $226 million and began developing the Model S, a sedan, launched in 2012.
In 2013, the production of the Model S was costly, and the shares depreciated by more than 20% when one of them caught fire. Elon Musk even offered to sell Tesla to Google for $11 billion, but sales improved, and the deal fell through. Tesla ended up being worth 100 times more than that eight years later.
During this time, the development of autopilot began, and in 2015, they launched the Powerwall, a home energy storage system, which received $800 million in orders in less than a week, with their SUV, the Model X, being launched at the end of that year.

A New Global Player
In 2016, Tesla entered the solar energy business by acquiring SolarCity, the largest solar panel installation company in the United States, for $2.6 billion, owned by Elon Musk’s cousins. At this point, Tesla was more than just a car manufacturer; it was a big tech player in renewable energy. They removed “Motors” from the name, and it became simply Tesla.
In 2017, they launched a more popular sedan, the Model 3, priced at $35,000, which attracted 325,000 reservations worldwide in the first week, leading Tesla’s market value to reach $50 billion and surpassing Detroit’s century-old giants: Ford, Chrysler, and General Motors.
The Model 3 allowed the company to scale up and transition from being a deficit to a profitable company in 2019 when it was producing 300,000 cars per year. Five years later, it produces six times that with a 20% margin, a feat previously achieved only by luxury car manufacturers like Ferrari.
While Ferrari has Formula 1 to showcase its brand, Tesla has Elon Musk, who in 2018 used his other company, SpaceX, to launch his Roadster into space, driven by a Starman listening to David Bowie. One of Tesla’s unique features is that, like Ferrari, it incurs zero marketing expenses, while Ford and Toyota spend $400 on advertising for every car sold.

A Sexy Brand
In 2020, the fifth model of the brand, the Y, a crossover between the X and the 3, was launched. In 2023, it surpassed the Toyota Corolla and became the world’s best-selling car. With this achievement, the company experienced its first four consecutive profitable quarters and joined the S&P 500, marking an important milestone in spelling “Sexy” with its models.
During the pandemic, Tesla’s stocks rose by 700% in one year, and its market value exceeded $1 trillion, making it the fifth-largest company in the United States. It not only became the largest car manufacturer in the world but also surpassed the combined value of the next 10 companies: Toyota, BYD, Volkswagen, leaving them all behind.
In late 2023, Tesla launched its post-apocalyptic pickup truck, the Cybertruck, the brand’s sixth model, with five of them still in production, except for the Roadster.

Tesla’s Assets
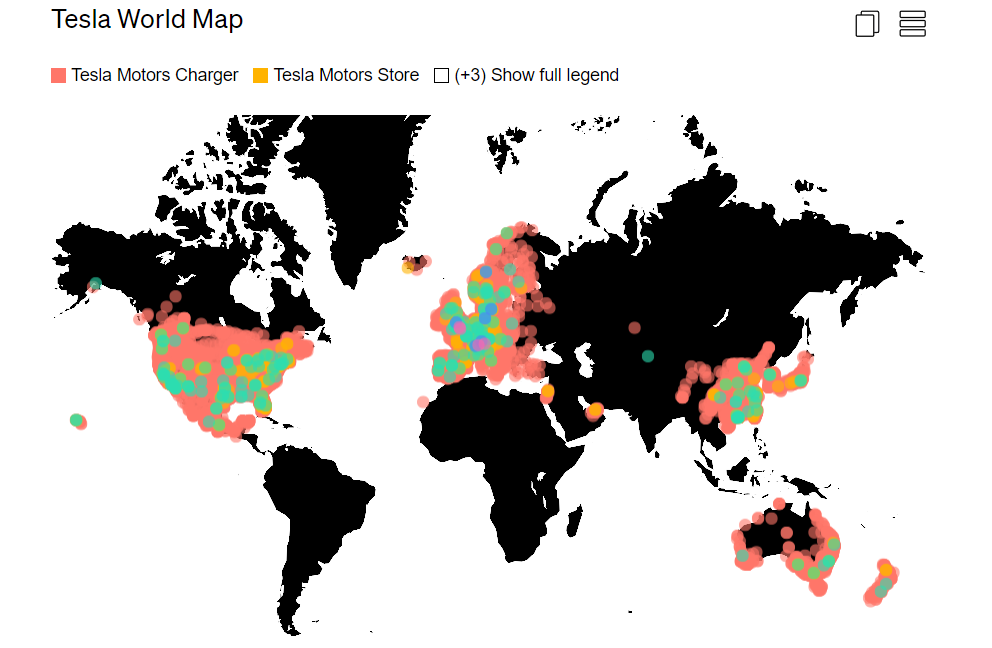
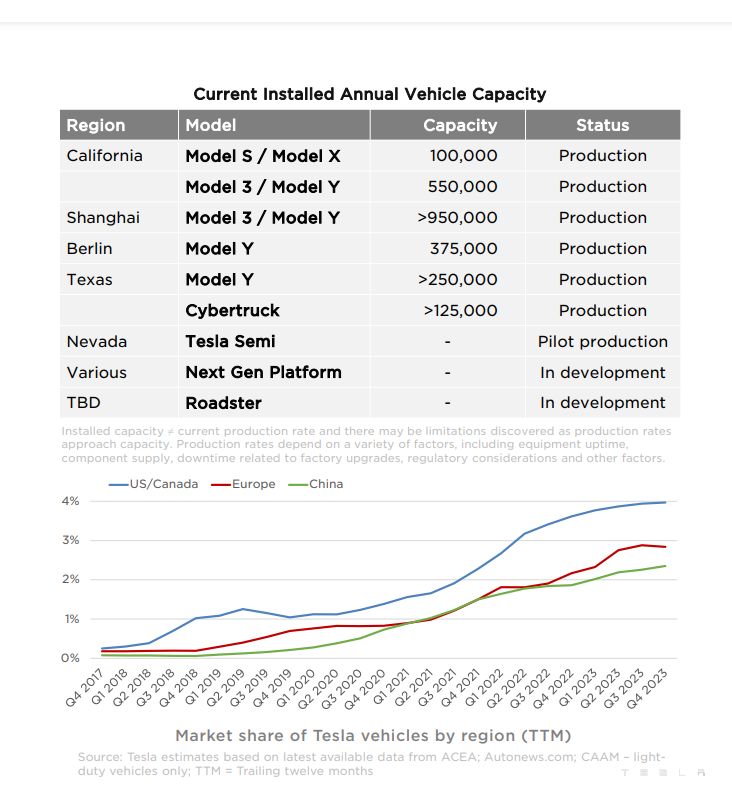
Tesla currently operates 7 Gigafactories in the United States, Germany, and China, where it produces key components for its vehicles on a large scale, as well as batteries and energy storage systems.
The company also owns a dozen smaller factories and over 1,200 stores worldwide, being the first American manufacturer to sell cars directly to consumers. Customers can order cars in-store, online, or via the website, with prices ranging from $40,000 to $100,000.
Tesla also operates 6,000 supercharger stations worldwide, located along highways, which provide 320 km of range with just 15 minutes of charging. Additionally, there are 55,000 connectors in residential areas, allowing owners to charge their vehicles overnight.

The Geography of Success
The bulk of Tesla’s sales come from the United States, where over half of the electric cars sold are Teslas, giving the company a 4% market share in the country, with almost 500,000 cars sold in 2023. Nearly half of Tesla’s revenue comes from its home country.
The second largest market is China, where the Shanghai Gigafactory produced over 600,000 vehicles in 2023, double the sales in the United States. However, this only accounts for half of the revenue, as Tesla sells its vehicles cheaper in China to compete with the local giant, BYD (Build Your Dreams). China already has the largest fleet of electric cars in the world, four times that of the United States and nearly half of the global total.
The third largest market for Tesla is Europe, where 30% of its revenue, $30 billion, came from the sale of 200,000 cars. In Norway, Tesla’s market share is already 23%, making it the country with the most Teslas per capita, and starting in 2025, Norway will only allow electric cars.
Performance of a Giant
85% of Tesla’s revenue comes from the sale of automobiles, with the remaining 15% coming from energy management and storage systems and services.
In 2023, the company sold 1.8 million cars [production image], a 35% increase compared to the previous year, with 1.2 million of those being the Y, the best-selling model, and half a million of the 3. Less than 5% of sales, or 70,000 vehicles, are from the high-end models, X and S.
Tesla is currently valued at $600 billion as of March 2024, making it the 11th largest company in the world, but it reached twice that amount in January 2022 when the stock hit $400. Today, it’s hovering around $200, and the company does not distribute dividends.
The Model 3 became the first electric car to surpass 1 million units sold in 2021, but Chinese competitors are catching up, with BYD even surpassing Tesla in the United States in 2022 by selling over half a million electric vehicles.
In Europe, the brand still faces competition from traditional manufacturers in the region, such as Renault. The future of Tesla will be more challenging now that electric cars have gained visibility and industry giants are heavily investing in this segment: Ford, GM, Nissan, as well as startups like Rivian.
Future Outlook
Today, Tesla has 140,000 employees worldwide, with few on the factory floor, as one of the company’s strengths is its highly mechanized assembly line. To date, 5 million Teslas have been produced, out of a global fleet of 26 million electric vehicles, and they aim to reach 10 million per year, which is the annual production of Volkswagen and Toyota combined.
Still within this decade, Tesla aims to achieve a self-driving car, a robot-taxi, the Semi truck, which is a pickup truck already in pilot project, with PepsiCo testing it. They are also set to launch a new Roadster, and the NextGen, an AI software that will come with the cars.

A Case of Success
A Tesla is one of the most incredible success stories on the stock market. It managed to surpass century-old companies that everyone thought were unbeatable, solely based on the vision of its members to create a future of sustainable mobility and their willingness to generate all the necessary infrastructure for it.
If you enjoyed this, give it a like and let me know in the comments which stocks and ETFs you’d like to see in this new playlist I’m creating for these assets.
This is not a recommendation to buy or sell Tesla. In the video below, I’ve provided an analysis for educational purposes on Tesla’s price charts:
